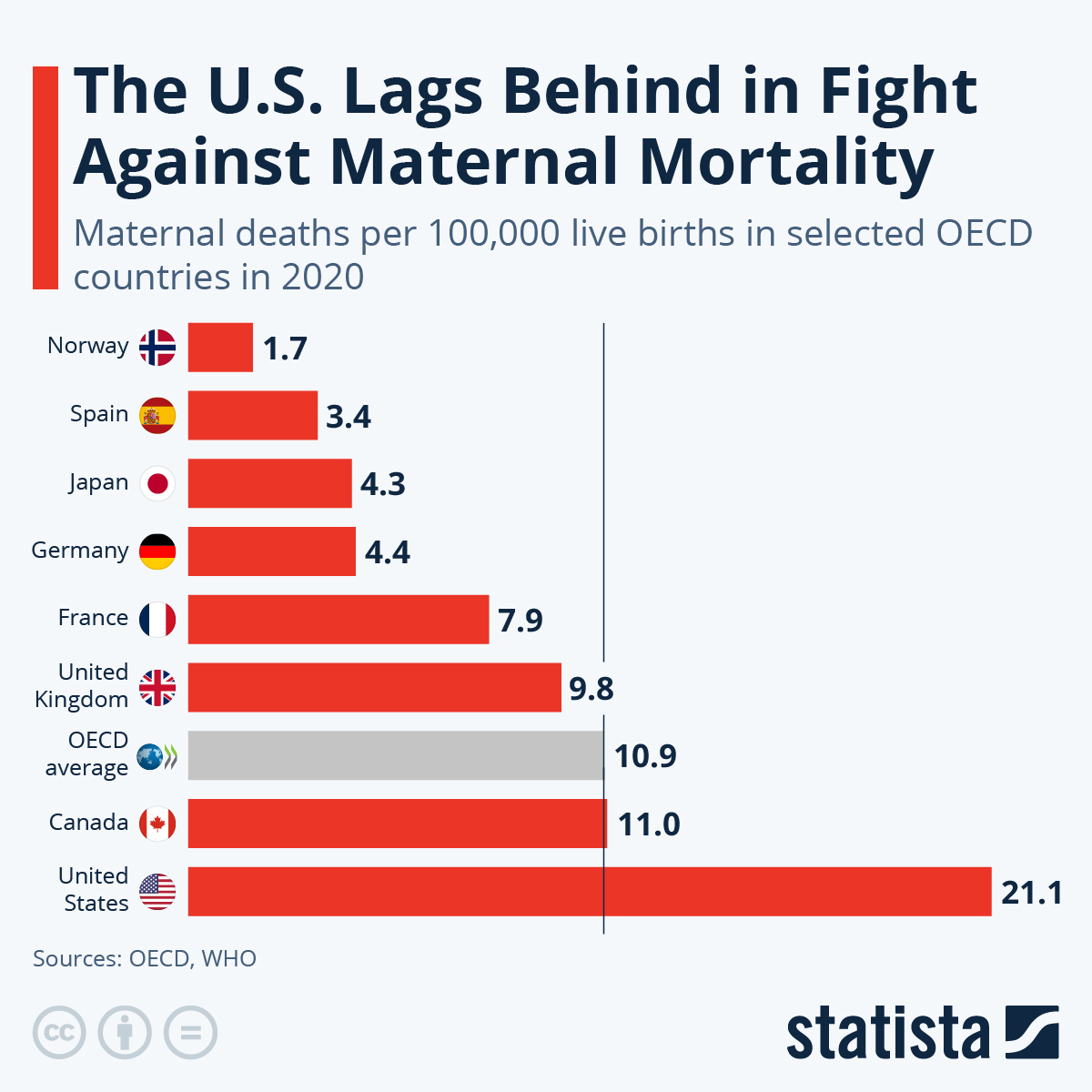
Maternal mortality is a pressing issue that continues to plague the United States, where more than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable. Despite being among wealthy nations, the U.S. holds the highest maternal mortality rates, a troubling statistic that has shown an alarming increase in recent years. According to recent studies, significant disparities exist across various states and demographic groups, highlighting the urgent need for reform in U.S. healthcare disparities. One of the primary contributors to these tragic outcomes includes cardiovascular disease during pregnancy, which represents a growing concern among maternal health experts. Addressing these issues through improved prenatal and postpartum care is critical to reversing the trend of preventable deaths and ensuring safer pregnancies for all women.
The phenomenon of maternal mortality—referring to deaths associated with pregnancy and childbirth—poses a significant challenge for healthcare systems worldwide, particularly in the U.S. This issue, marked by a rise in pregnancy-related fatalities, brings to light the considerable healthcare disparities that affect women of differing racial and ethnic backgrounds. Observations indicate that conditions such as cardiovascular complications during pregnancy are increasingly responsible for these fatalities, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced postpartum care. Furthermore, the rate of preventable deaths highlights systemic failures that require immediate attention. A holistic approach, one that prioritizes comprehensive care during the entire perinatal period, is essential for overcoming these challenges.
Understanding U.S. Maternal Mortality Rates
Maternal mortality rates in the United States remain alarmingly high, especially compared to other high-income nations. Recent studies report a continued rise in pregnancy-related deaths, with more than 80 percent of these fatalities deemed preventable. The U.S. healthcare system’s complexities, characterized by disparities in access and quality of care, play a significant role in this public health crisis. Research indicates that racial and ethnic disparities significantly impact maternal outcomes, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts.
Moreover, the variations in state-level data highlight systemic inequalities, underscoring the need for targeted policy interventions. For instance, if all states performed at the level of California, a substantial number of pregnancy-related deaths could be thwarted. Understanding these disparities is crucial for informing effective healthcare strategies and addressing the urgent need for comprehensive maternal health policies that encompass every stage of the pregnancy continuum, including postpartum care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the leading causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
The leading cause of maternal mortality in the U.S. is cardiovascular disease, accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. Other significant factors include hemorrhage, hypertension, and conditions associated with pre-eclampsia and eclampsia.
Why does the U.S. have a higher maternal mortality rate compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has a higher maternal mortality rate due to various factors, including a fragmented healthcare system, disparities in access to care, and the prevalence of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease among reproductive-age individuals.
What percentage of pregnancy-related deaths are considered preventable?
Studies indicate that more than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, highlighting the necessity for improved healthcare access and better postpartum care.
How do U.S. healthcare disparities affect maternal mortality rates?
U.S. healthcare disparities significantly impact maternal mortality rates, with racial and ethnic minorities experiencing disproportionately higher rates of pregnancy-related deaths due to systemic inequities in healthcare access and quality.
What role does postpartum care play in reducing maternal mortality?
Improving postpartum care is critical for reducing maternal mortality. Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum, account for nearly a third of all pregnancy-related deaths, emphasizing the need for extended care beyond the initial postpartum period.
What is the impact of cardiovascular disease during pregnancy on maternal mortality?
Cardiovascular disease has become a leading cause of maternal mortality. The rising incidence of conditions like hypertension during pregnancy poses significant risks, especially for younger women in their childbearing years.
How can we reduce state-level variations in maternal mortality rates?
To reduce state-level variations in maternal mortality rates, it’s essential to address policy disparities, implement best practices from states with lower rates, and invest in public health infrastructure to support comprehensive maternity care.
Why is tracking late maternal deaths important for maternal health?
Tracking late maternal deaths is crucial as it provides a more comprehensive understanding of maternal mortality. Recognizing that postpartum recovery extends beyond 42 days allows for improved healthcare policies and support during this vulnerable time.
What are some challenges in addressing maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Challenges in addressing maternal mortality include inconsistent data collection, a lack of investment in public health infrastructure, and systemic inequities in healthcare access, all of which need urgent attention to improve maternal health outcomes.
What strategies can improve the quality of care for pregnant individuals?
Improving the quality of care for pregnant individuals can be achieved by increasing access to prenatal and postpartum services, addressing healthcare disparities, and investing in innovative healthcare solutions that prioritize maternal health.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rates | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates rising from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 by 2022. |
| Disparities in Mortality | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates, nearly four times higher than white women, reflecting significant racial disparities. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase in maternal deaths occurred in 2021, likely linked to the COVID-19 pandemic, indicating a deterioration in health outcomes. |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Cardiovascular issues are the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, now accounting for over 20% of these deaths. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy, highlighting the need for long-term postpartum care. |
| Healthcare System Challenges | Issues such as a patchwork healthcare system, inequitable policies, and racial discrimination contribute to the high maternal mortality rates. |
| Need for Policy Changes | Investment in public health infrastructure and policies aimed at reducing disparities are crucial to improving maternal health outcomes. |
Summary
Maternal mortality remains a pressing issue in the United States, with rates increasing in recent years despite the fact that many pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. Addressing the disparities and underlying causes, such as healthcare access and chronic conditions, is essential for improving maternal health outcomes. Effective policy changes and investment in comprehensive care during and after pregnancy are critical steps toward reducing these alarming trends.